Effective Multi-shot Person Re-identification through Representative Frames Selection and Temporal Feature Pooling:
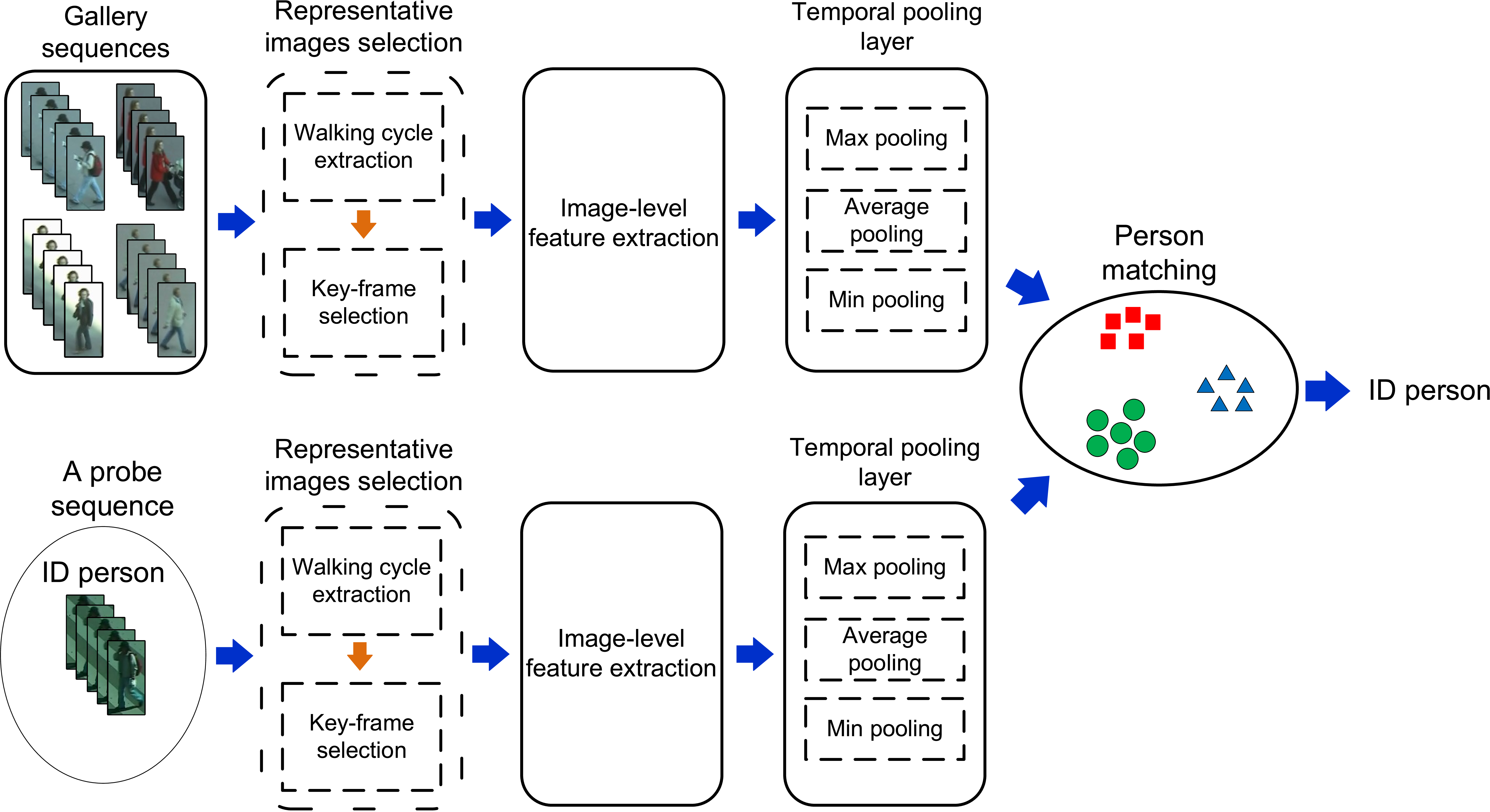
The proposed framework consists of four main steps: representative image selection, image-level feature extraction, temporal feature pooling and person matching
|
Multi-shot person re-identification (ReID) is a popular case of person ReID in which a set of images are processed for each person.
However,using entire image set for person ReID as most experimented proposals is not always effective because of time and memory consuming.
The main contribution of this work is the proposed strategies for (1) choosing representative image frames for each individual instead of
entire set of frames, and (2) temporal feature pooling in multi-shot person ReID.
These strategies are efficiently integrated in a person ReID framework which uses GoG (Gaussian of Gaussian)
and XQDA (metric learning Cross-view Quadratic Discriminant Analysis) for person representation and matching.
The effectiveness of the proposed framework on two benchmark datasets (PRID 2011 and iLIDS-VID) in terms of re-identification accuracy,
computational time, and storage requirements are deeply investigated and analyzed.
The experimental results allow to provide several recommendations on the use of these schemes based on the characteristics of the
working dataset and the requirement of the applications.
Furthermore, the study also offers a desktop-based application for person search and ReID.
The implementation of the proposed framework will be made publicly available.
|
|
Publications:
Thuy-Binh Nguyen, Thi-Lan Le*, Louis Devilliane, Thi Thanh Thuy Pham, Ngoc-Nam Pham, Effective Multi-shot Person Re-identification through Representative Frames Selection and Temporal Feature Pooling, Multimedia Tools and Applications
|
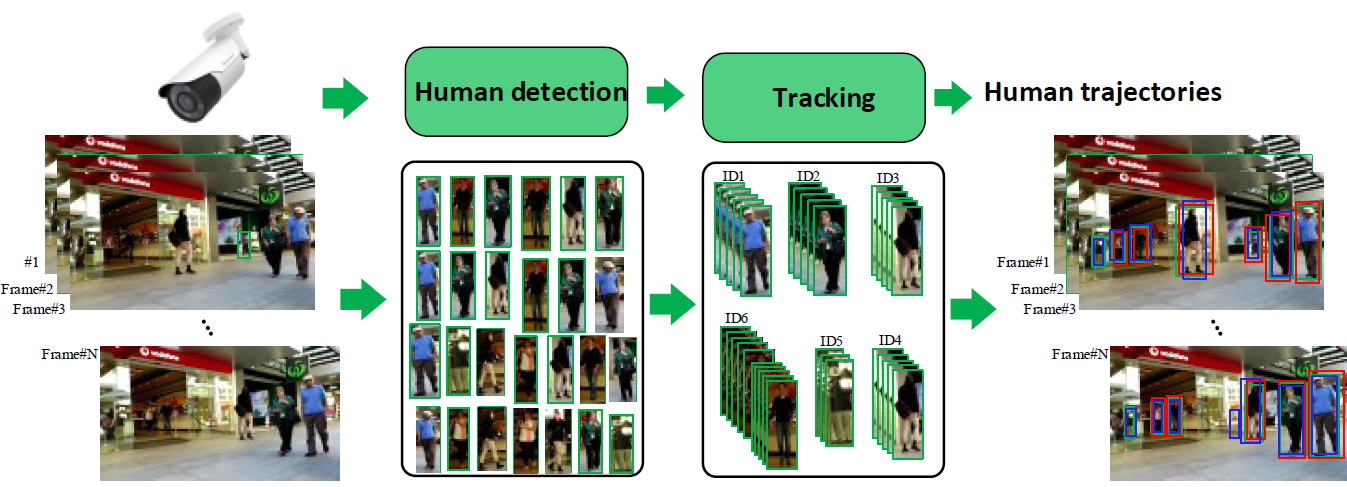
Comparative evaluation of human detection and tracking approaches for online tracking applications
:
|
Object detection and tracking in videos is an important problem in computer vision thanks to its wide applications in various video analysis scenarios. As a result, it has attracted huge interest from the scienti?c community. Majority of recent works following the tracking-by-detection approaches which rely on a people detector to start, update, reinitialize, guide and terminate the trackers. Recent years have witnessed a signi?cant advance in person detection and tracking performance. However, person detection and tracking are usually treated separately in the recent works. The contributions of this paper are twofold. First, a comparative evaluation of the coupling of person detection and tracking methods for online tracking applications is conducted on two video datasets: MOT17 - a benchmark dataset provided in MOT Challenge [1] and our own dataset captured in a video surveillance context. For this, we investigate a popular online tracking method (DeepSORT) coupled with the two state-of-the-art people detection methods that are You Only Look Once ( YOLO) and MaskR-CNN. Second, a deep analysis on the behavior of the person detection and tracking method in term of both detection and tracking performance and resources requirement for practical applications is given. The implementation of the framework and dataset used in this paper will be made publicly available.
|
|
Publications:
Hong-Quan Nguyen, Thuy-Binh Nguyen, Tuan-Anh Nguyen, Thi-Lan Le, Thanh-Hai Vu, Alexis Noe, Comparative evaluation of human detection and tracking approaches for online tracking applications
, 2019 International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Communications (ATC)
|
A Quantitative Analysis of the Effect of Human Detection and Segmentation Quality in Person
Re-identification Performance:
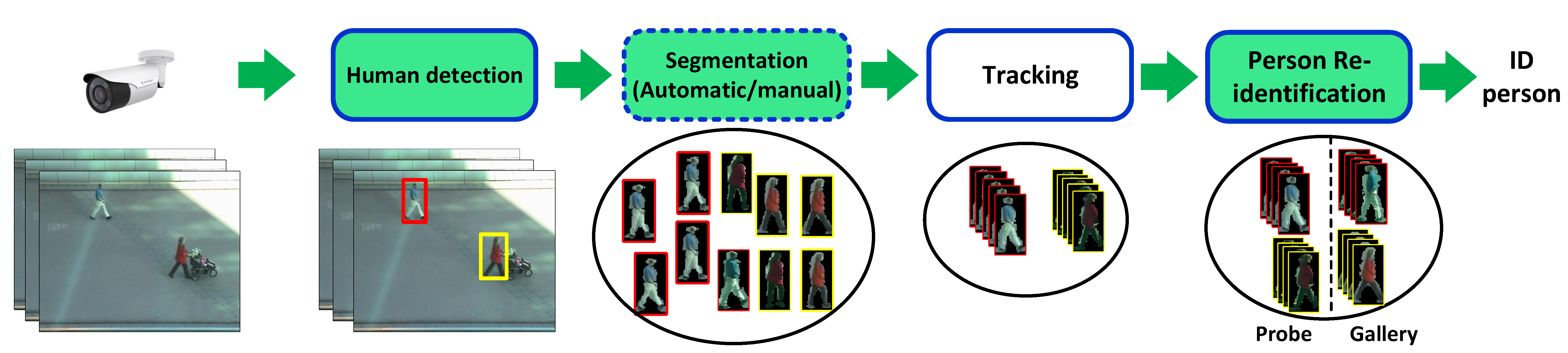
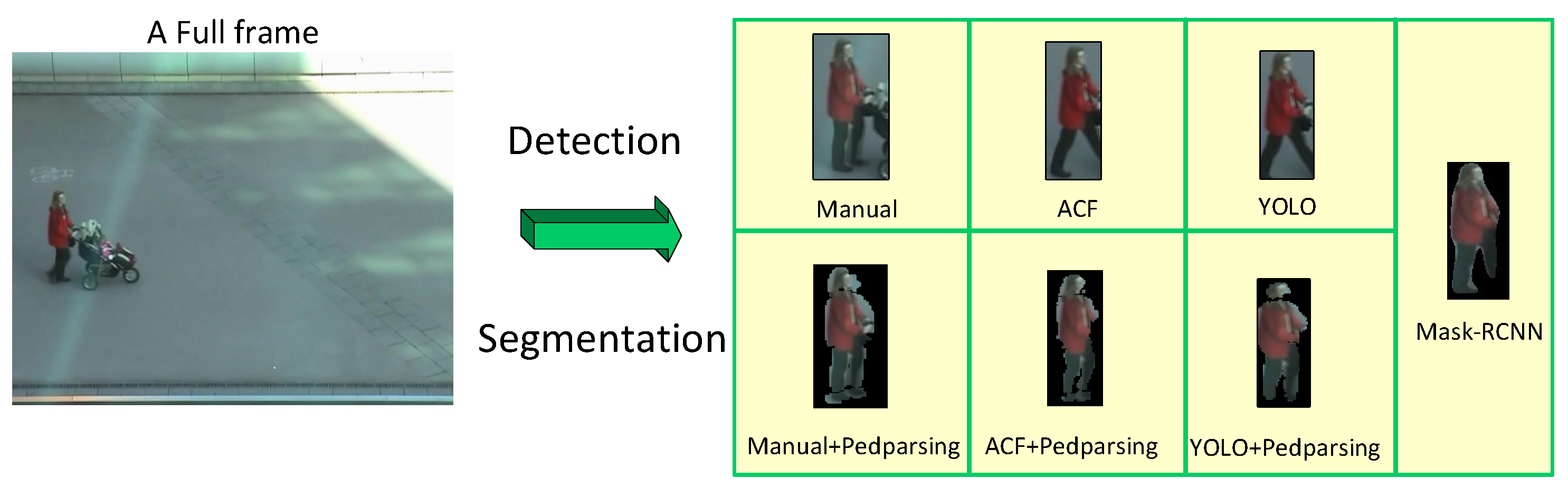
An example for automatic person detection and segmentation results on PRID 2011 dataset.
|
Person re-identification, a problem of person identity association across camera views at different locations and times, is the second step in two-steps system for automatic
video surveillance: person detection, tracking and person reidentification. However, most of the reported person Re-ID methods deal with the human regions of interest (ROIs) which
are extracted manually with well-aligned bounding boxes. They mainly focus on designing discriminative feature descriptors and
relevant metric learning on these manually-cropped human ROIs. This paper aims at answering two questions: (1) Do human detection and segmentation affect the performance of person reidentification?;
(2) How to overcome the effect of human detection and segmentation with the state of the art method for person re-identification? To answer these two question, quantitative
evaluations have been performed for both single-shot and multishot scenarios of person re-identification. Different state-of-theart
methods for human detection and segmentation have been evaluated on two benchmark datasets (VIPeR and PRID2011). The obtained results allow to give some suggestions for developingfully automatic video surveillance systems.
|
|
Publications:
Thuy-Binh Nguyen, Hong-Quan Nguyen, Thi-Lan Le, Thi Thanh Thuy Pham and Ngoc-Nam Pham, A Quantitative Analysis of the Effect of Human Detection and Segmentation Quality in Person Re-identification Performance, 2nd Int. Conference on Multimedia Analysis and Pattern Recognition (MAPR), May, 2019
|
C++ implementation of Gaussian and Gaussian (GOG) feature:
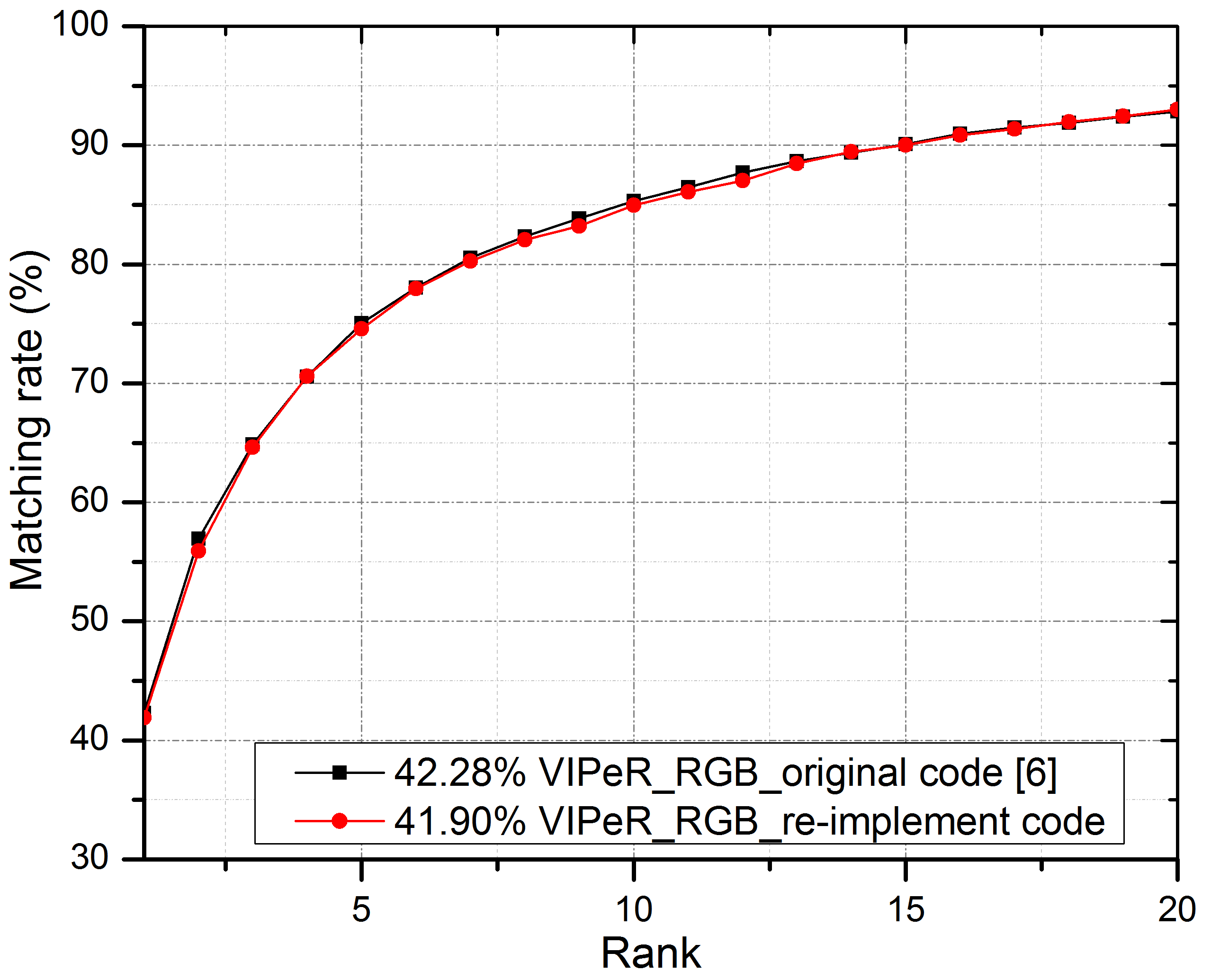
Obtained CMC curves on VIPeR dataset with our new implementation and the authors source code
|
We make use of Gaussian of Gaussian (GOG) in practical by providing simultaneously two improvements.
First, we re-implement and perform intensive experiments to select the optimal values of the parameters using in GOG feature extraction.
Second, we propose and apply pre-processing techniques on person images.
The experimental results show that the proposed approach allows to extract GOG 2 times faster than the available source code and achieve remarkably high accuracy for person ReID.
The obtained accuracies at rank-1 on VIPeR dataset are 51.75% (with background) and 55.79% (without background).
|
|
Publications:
NGUYEN Thuy-Binh, TRAN Duc-Long, LE Thi-Lan, Pham Thi-Thanh Thuy, Doan Huong-Giang, Towards a practical use of Gaussian of Gaussian descriptor for person re-identification, The 5th NAFOSTED Conference on Information and Computer Science (NICS 2018)
[code]
|
Fully-automated person re-identification system:
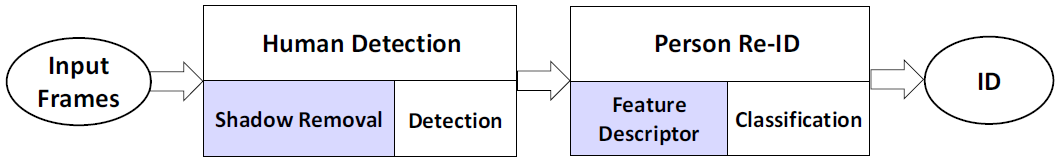
A diagram of fully-automated vision-based person Re-ID system
|
While most current works base on the assumption that person detection is perfect (determined manually). In this work, we focus on fully-automated person re-identification. The proposed work follows image-to-video strategy.
For each person, we build a robust model based on adaptive Kernel Descriptor from hand-defined/automatically detected boxes and then use SVM to learn the model for this person.
Comparison of our proposed method with state of the art methods on different datasets.
|
|
Publications:
Thanh-Thuy Pham, Thi-Lan Le, Hai Vu, Trung-Kien Dao, Van-Toi Nguyen, Fully-automated person re-identification in multi-camera surveillance system with a robust kernel descriptor and effective shadow removal method, Image and Vision Computing, 2017
Thanh-Thuy Pham, Thi-Lan Le, Trung-Kien Dao, Duy-Hung Le, A robust model for person re-identification in multimodal person localization, in The Ninth
International Conference on Mobile Ubiquitous Computing, Systems, Services and Technologies (UBICOMM 2015), 2015, p. 51
Thi Thanh Thuy Pham, Thi-Lan Le, Trung-Kien Dao, Person Re-Identification for Non-overlapping Cameras in Multimodal Person Localization, International Journal On Advances in Systems and Measurements, v 9 n 1&2 2016.
|
A reliable image-to-video person re-identification based on feature fusion:
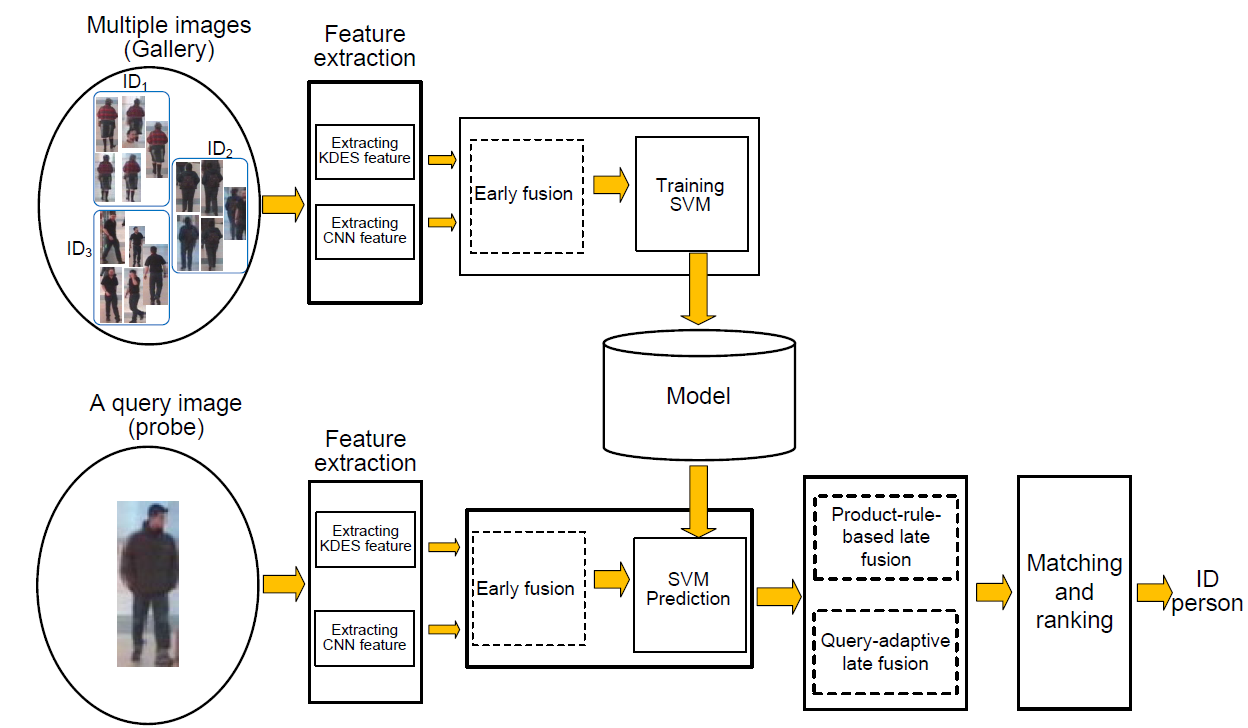
The proposed framework for the image-to-video person re-identification
|
We formulate
person re-id problem as a classification-based information retrieval where a person appearance model is learned in the training phase and the identity of an interested person is determined by the probability that his/her
probe image belongs to the model. To learn the person appearance model, two features that are Kernel descriptor (KDES) and Convolution Neural
Network (CNN) are investigated. Then, three fusion schemes including early fusion, product rule and query-adaptive late fusions are proposed.
Extensive experiments have been conducted on two public benchmark datasets: CAVIAR4REID and RAID
|
|
Publications:
NGUYEN Thuy-Binh, LE Thi Lan, NGUYEN Dinh-Duc, PHAM Dinh-Tan, A reliable image-to-video person re-identification based on feature fusion, 10th Asian Conference on Intelligent Information and Database Systems (ACIIDS), Springer - march 2018
|
|
Interesting links:
- Our datasets for person re-identification: MICA
- Available dataset for person re-identification: http://robustsystems.coe.neu.edu/sites/robustsystems.coe.neu.edu/files/systems/projectpages/reiddataset.html
- Current results for person re-identification: http://www.ssig.dcc.ufmg.br/reid-results/
- Re-id Resources: https://wangzwhu.github.io/home/re_id_resources.html
|






