Reasearch Topics: Human in a Surveillance Camera Network
Video Capsule Endoscopy Analysis |
Computer Vision in Agricultural Engineering and Biodiversity |
Vision-based
system
|
Human Computer Interaction |
| Vision-based Localization in a camera network | |
 |
In this paper, a
fully-automated person Re-ID (Re-identification) system is proposed
for real scenarios of human tracking in non-overlapping camera
network. The system includes two phases of human detection and
Re-ID. The human ROIs (Regions of Interest) are extracted from human
detection phase and then feature extraction is done on these ROIs in
order to build human descriptor for Re-ID. Unlike other approaches
which deal with manually-cropped human ROIs for person Re-ID, in
this system, the person identity is determined based on the human
ROIs extracted automatically by a combined method of human
detection. Two main contributions are proposed on both phases of
human detection and Re-ID in order to enhance the performance of
person Re-ID system. First, an effective shadow removal method based
on score fusion of density matching is proposed to get better human
detection results. Second, a robust KDES (Kernel DEScriptor) is extracted from human ROI for person classification. Additionally, a new person Re-ID dataset is built in real surveillance scenarios from multiple cameras. The experiments on benchmark datasets and our own dataset show that the person Re-ID results using the proposed solutions outperform some of the state-of-the-art methods. |
|
|
| Human tracking and linking trajectories in a surveillance camera network | |
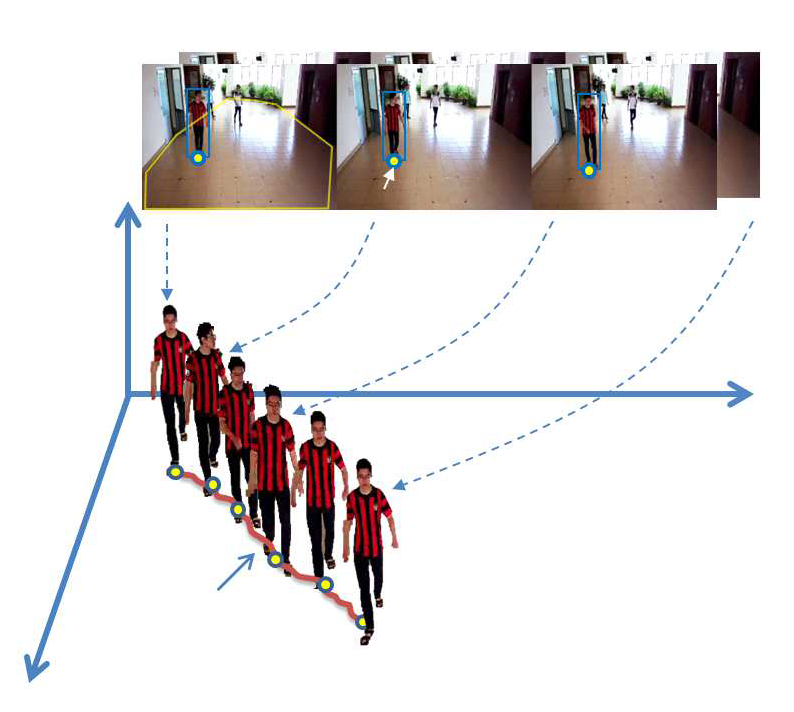 |
We propose a high
accuracy solution for locating pedestrians from video streams in a
surveillance camera network. For each camera, we formulate the
vision-based localization service as detecting foot-points of
pedestrians in the ground plane. We address two critical issues that
strongly a ect the foot-point’s detection results: casting shadows
and pruning detection results due to occlusion. For the rst issue,
we adopt a removing shadow technique based on a learning-based
approach. For the second issue, a regression model is proposed to
prune the wrong foot-point detection results. The regression model
plays a role in estimating the position by using the human factors
such as height, width and its ratio. A correlation of the detected
foot-points and the results estimated from the regression model is
examined. Once a foot-point is missed due to uncorrelation problem,
a Kalman lter is deployed to predict the current location. To link
the trajectory of the human in the camera network, we base on an
observation about the same ground-plane/ oor in view of cameras then
the transformation between a pair of cameras could be computed o
ine. In the experiments, a high accuracy performance for locating
the pedestrians and a real-time computation are achieved. The proposed method therefore is particularly feasible to deploy the vision-based localization service in scalable indoor environments such as hall-way, squares in public buildings, o ces, where surveillance cameras are common used. |
|
|
| Abnormality behavior detection [to be updated ...] | |
|
|
|