Reasearch Topics: Vision-based system supporting visually impaired people
Video Capsule Endoscopy Analysis |
Computer Vision in Agricultural Engineering and Biodiversity |
Human Computer Interaction |
Human in a Surveillance Camera Network |
| Obstacle Detection and Distance estimation using monocular camera in nagivation service for visually impaired people | |
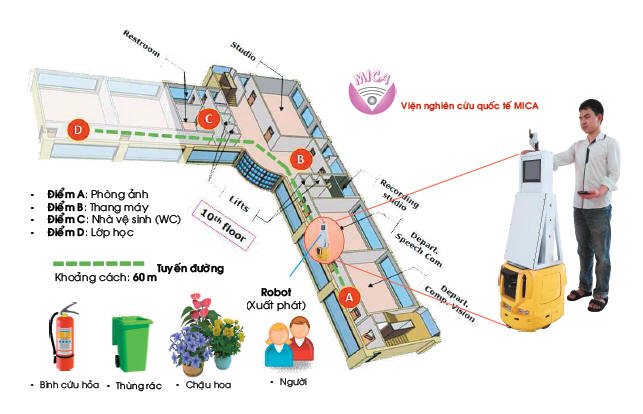 |
In this paper, we
propose a method for obstacle detection and distance estimation
using monocular camera mounted on a mobile robot. The proposed system aims to support visually impaired people navigating in indoor environ-ment. The obstacles include static and dynamic objects on that encumber human mobility. For static objects, supporting information such as type of object, positions, and corresponding images in relevant scenes are stored in database (DB). To detect them, the images captured during robot’s movements are compared with the corresponding images through a localization algorithm proposed in [1]. Then the existing objects in DB will be identified and distances from them to current robot’s position is estimated. For dynamic objects, such as movements of people in scenes, we use HOG-SVM algorithm [2]. To estimate distance from camera to detected obstacles, we utilize a disparity map which is built from consecutive frames. The experiments are evaluated in the hall of building floor of 60 meters under different lighting conditions. The results confirm that the proposed method could exactly detect and esti-mate both static and dynamic objects. This shows the feasibility to help visually impaired people avoiding obstacles in navigation. |
|
|
Indoor assistance for visually impaired people using a RGB-D camera |
|
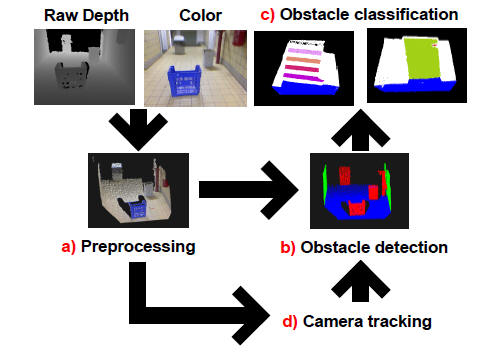 |
In this paper a
navigational aid for visually impaired people is presented. The
system uses a RGB-D camera to perceive the environment and
implements self-localization, obstacle detection and obstacle
classification. The novelty of this work is threefold. First,
self-localization is performed by means of a novel camera tracking
approach that uses both depth and color information. Second, to
provide the user with semantic information, obstacles are classified
as walls, doors, steps and a residual class that covers isolated
objects and bumpy parts on the floor. Third, in order to guarantee
real time performance, the system is accelerated by offloading
parallel operations to the GPU. Experiments demonstrate that the
whole system is running at 9 Hz. |
|
|
Geometry-based 3D Object Fitting and Localization in Grasping Aid for Visually Impaired People |
|
 |
This paper presents a geometry-based method for 3D object fitting and localization in the context of building a grasping aid service for visually impaired people using information from Kinect sensor. Given two constraints of this working application, (1) the interested object is on a table and (2) the geometrical form of the object is known in advance based on the query of the user, the proposed system consists of three steps: table plane detection, object detection, and object fitting and localization. Our work has three contributions. First, we propose to use organized point cloud representation instead of just point cloud in order to speedup the computational time and improve the accuracy of table plane detection. Second, we employ MLESAC (Maximum LikElihood SAmple Consensus) that can give better results for object fitting. Third, we introduce a new method for evaluating object localization task and make a quantitative evaluation of object localization on our captured dataset. |
|
|
Mapping Services in Indoor Enviroments |
|
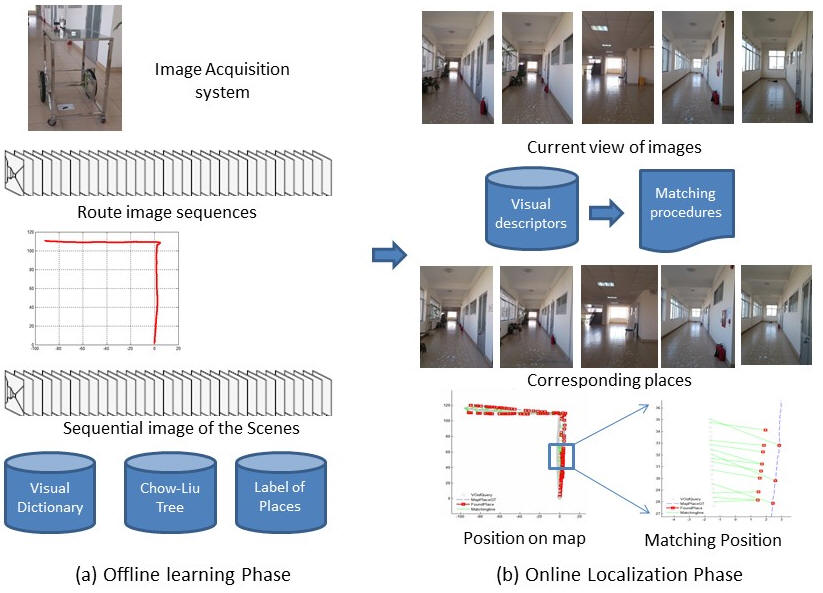 |
This paper describes a
visual-based system that autonomously operators for both map
building and localization tasks. The proposed system is to assist
mapping services in small or mid-scale environments such as inside a
building or campus of school where conventional positioning data
such as GPS, WIFI signals are often not available. Toward this end,
the proposed approaches utilize only visual data. We design an image
acquisition system for data collections. On one hand, a robust
visual odometry method is utilized to create routes in the
environment. On the other hand, the proposed approaches utilize
FAB-MAP (Fast Appearance Based Mapping) algorithm that is maybe the most successful for recognizing places in large scenarios. The building route and learning visited places are offline process in order to represent a map of environment. Through a matching image-to-map procedure, the captured images at current view are continuously positioned on the constructed map. This is an online process. The proposed system is evaluated in a corridor environment of a large building. The experimental results show that the constructed route coincides with ground truth, and matching image-to-map is high confidence. The proposed approaches are feasible to support visually impaired people navigating in the indoor environments. |
|
|
A Visual SLAM system on mobile robot supporting visually impaired people |
|
 |
This paper describes a Visual
SLAM system developed on a mobile robot in order to support
localization services to visually impaired people. The proposed
system aims to provide services in small or mid-scale environments
such as inside a building or campus of school where conventional
positioning data such as GPS,WIFI signals are often not available.
Toward this end, we adapt and improve existing vision-based techniques in order to handle issues in the indoor environments. We firstly design an image acquisition system to collect visual data. On one hand, a robust visual odometry method is adjusted to precisely create the routes in the environment. On the other hand, we utilize the Fast-Appearance BasedMapping algorithmthat is may be the most successful for matching places in large scenarios. In order to better estimate robot’s location, we utilize a Kalman Filter that combines the matching results of current observation and the estimation of robot states based on its kinematic model. The experimental results confirmed that the proposed system is feasible to navigate the visually impaired people in the indoor environments |
|
|