Image and Video Understanding
Natural lines detection for image representation | This work has been conducted in the context of my master and Ph.D
thesis at GRAVIR laboratory, Inria Rhone-Alpes, Monbonnot, France under
the surpervision of Prof. Augustin Lux from 09/2001 to 06/2006. In this
work, we have proposed a new definition of ridge and valley that bases
on analysis of Laplacian response of the image in the scale
space. Hereby, we detected ridges and valleys as local directional
maxima of Laplacian. These ridges and valleys correspond
to the central axes of structures with additional information of width. Ridges
and valleys show its significant advantages for representation of all natural line
structures. We have applied into text and human detection in
images and obtained very good results [more detail ... ] |
Visual localization and mapping 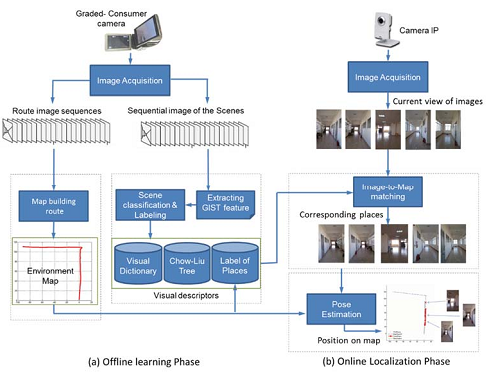 | This research was carried out in the framework of Ph.D thesis of Quoc-Hung Nguyen under my supervision and Prof. Quang-Hoan Nguyen from 12/2010 to 12/2016 at Hanoi University of Science and Technogy. In this work, we have three main contributions: i) proposed a hybrid representation of environment for visual servoing; ii) enriched keypoints detected from images of floor planes for improving visual servoing algorithm; iii) improved vision based localization in indoor environment by discarding similar images and keeping only distintive key location. The experiments have been conducted in three environments: a floor of B1 building; a floor of Ta Quang Buu library, and a floor of Nguyen Dinh Chieu school. We have sucessfully built an application that support the visually impaired to navigate in indoor environment using robot [more detail ... ]. |
Object detection and fitting from point cloud data 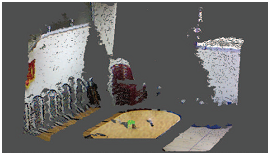 | We
proposed a geometry-based method for 3D object fitting and localization
in the context of building a grasping aid service for visually impaired
people using information from Kinect sensor. Given two constraints of
this working application, (1) the interested object is on a table and
(2) the geometrical form of the object is known in advance based on the
query of the user, the proposed system consists of three steps: table
plane detection, object detection, and object fitting and localization.
Our work has three contributions. First, we propose to use organized
point cloud representation instead of just point cloud in order to
speedup the computational time and improve the accuracy of table plane
detection. Second, we employ MLESAC (Maximum LikElihood SAmple
Consensus) that can give better results for object fitting. Third, we
introduce a new method for evaluating object localization task and make
a quantitative evaluation ofobject localization on our captured
dataset [more detail ... ] |
Image analysis in biodiversity   | We
applied and improved image processing techniques for three main
biordiversity applications. The first is a system for automated
classification of rice variety for rice seed production. We
investigated various feature extraction techniques for efficient rice
seed image representation. We analyzed the performance of powerful
classifiers on the extracted features for finding the robust one.
Images of six different rice seed varieties in northern Vietnam were
acquired and analyzed. This result can be used for developing a
computer-aided machine visionsystem for automated assessment of rice
seeds purity . The second application is to count tender tea shoots in
a sampled area is required before making a decision for plucking.
However, it is a tedious task and requires a large amount of time. In
this paper, we propose a vision-based method for automatically
detecting and counting the number of tea shoots in an image acquired
from a tea field. It offers an elegant way to build an assisting
tool for tea harvesting. The third application is to identify medicial
plant using multimodal information [more detail ... ] |
Human detection and tracking  | Object
tracking becomes a problem that interests more and more
researchers due to its wide applications in reality. In monitoring
application where we need to detect and track multiple people in a scene,
multiple object tracking is necessary.
The problem of multiple object
tracking is much more complex
than single object tracking because we must do an
additional step: data association as well as manage
the apparition and disappearance of the objects. In this work, we
proposed to detect human in a fast and efficient manner. First, we
applied a backgound substraction to decarding all static regions in
images and keep only moving regions of interest (ROI), then we verify
if ROI contains a human by HOG-SVM human detector. For human
tracking, we proposed a framework for multiple
objects tracking using Kalman filter
with the data association using
histogram based similarity measurement. This method
permits tracking multiple people in realtime so can be applied in real
applications [more detail ... ] |
Human activity representation and recognition 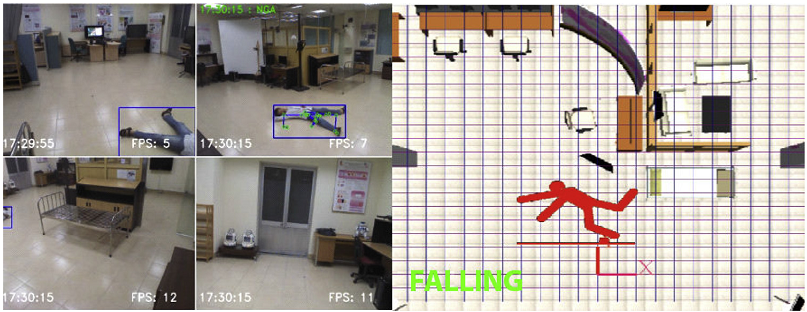 | In this study, we overcome these encountered issues by combining multi-modal features (skeleton and RGB) from Kinect sensor to take benefits of each data characteristic. If a skeleton is available, we propose a rules based technique on the vertical velocity and the height to floor plane of the human center. Otherwise, we compute a motion map from a continuous gray-scale image sequence, represent it by an improved kernel descriptor then input to a linear Support Vector Machine. This combination speeds up the proposed system and avoid missing detection at an unmeasurable range of the Kinect sensor. We then deploy this method with multiple Kinects to deal with large environments based on client server architecture with late fusion techniques. We evaluated the method on some freely available datasets for fall detection. Compared to recent methods, our method has a lower false alarm rate while keeping the highest accuracy. We also validated on-line our system using multiple Kinects in a large lab-based environment. Its on-line deployment on multiple Kinects shows the potential to be applied in to any of living space in reality [more detail ... ] |
Tracking for augmented reality 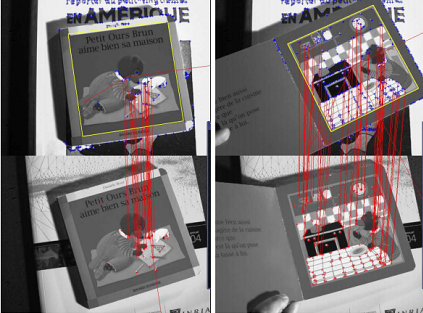 | This
paper develops a fully automatic system for tracking based on matching
keypoints at both steps: initialization and tracking. At
initialization, the pose of the camera is reliably estimated by
matching the first image against all reference images in database using
SIFT-matching algorithm [1]. Then we apply a fast algorithm, proposed
in our previous
works [9] to match the current image with the previous one to speed up
the tracking. In case where the matching is not satisfied, SIFT
matching is applied to re-initialize the tracker. The main contribution
of this paper is having developed one system of camera tracking, which
is fully automatic and works in near real-time, so suitable to
real-time applications such as augmented reality that we show the
result in this paper [more detail...] |
Vision based Human Machine Interaction
Hand posture recognition for human robot interaction  | Hand posture recognition is an extremely active research topic in Computer Vision and Robotics, with many applications
ranging from automatic sign language recognition to human-system
interaction. We have performed this work in in the context of Ph.D
Thesis of Van-Toi Nguyen. We have made three contributions: For
hand detection: we introduced internal Haarlike features that are
detected only in the region of the hand. This method outperform the
Viola-Jone method on the same dataset. For hand representation, a new descriptor for hand representation based
on the kernel method (KDES) has been proposed which is more robust to scale change, rotation, and differences in the object
structure. We have built an application which uses hand postures for controlling robot in the library [more detail ... ] |
Dynamic hand gesture recogniton and application into human system interaction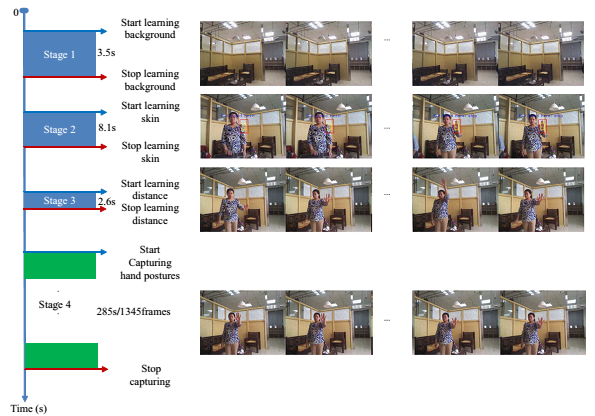 | This
work tackles a new prototype of dynamic hand gestures and its
advantages to apply in controlling smart home appliances. The proposed
gestures convey cyclical patterns of hand shapes as well hand
movements. Thanks to the periodicity of defined gestures, on one hand,
some common technical issues that may appear when deploying the
application (e.g., spotting gestures from a video stream) are
addressed. On the other hand, they are supportive features for
deploying robust recognition schemes. To this end, we propose a novel
hand representation in temporal-spatial space. Particularly, the phase
continuity of the gesture’s trajectory is taken into account underlying
the conducted space. This scheme obtains very competitive results with
the best accuracy rate is of 96%. We deploy the proposed techniques to
control home-appliances such as lamps, fans. Such systems have been
evaluated in both lab-based environment and real exhibitions. In the
future, the proposed gestures will be evaluated in term of naturalness
of end-users and/or robustness of the systems [more detail ... ] |
Face detection and recognition  | This
work concerns the problem of face recognition from video under
uncontrolled lighting condition. To face with illumination change, we
propose to inspire the idea that preprocesses input images in order to
represent them robust to illumination change [1]. We then use embedded
Hidden Markov Model (EHMM), a famous model for face recognition to
identify faces [2]. The main reason that we would like to study and
experiment this model is that it allows us to represent structure of
face images that makes more explicit face representation than numeric
face descriptors. The traditional EHMM was applied to face recognition
from still images. In our paper, we deal with face recognition from
video. Therefore, we propose to combine the recognition result obtained
from several frames to make our decision more confident. This improves
significantly the recognition rate. We have trained our model and
tested with two face databases, the one is the Yale-B database and the
other oneis created by MICA Institute |